While this access is limited to onsite research visits, access to such a collection is unique and has great potential to impact research as previously shown. ppThe Sigma Sound Studios Collection consists of magnetic tape sound recordings. These recordings take the form of multi-track music productions, mono and stereo mix-downs, multi-track and stereo advertisement productions, stereo live-in-studio radio broadcasts and multi-track film soundtrack productions. These 6119 audiotapes consist of masters, safeties and alternate takes of twelve different formats that are represented in Figure 4.
ppimg src"http:arpjournal.
How does vav reheat work/
Pros and Cons of VAV Systems
Schnackel Engineers
VAV Reheat
Stencil: Zone How does vav reheat work Stencil: Grp-VAV w/reheat
Type: Air Terminal
Sub Type: VAV_Reheat
![]()
Note: Requires a connection to a hot water loop
EnergyPlus IDF Objects
EnergyPlus Object - AirTerminal:SingleDuct:VAV:Reheat
Variable air volume (VAV) systems control the dry-bulb temperature inside a zone by varying the supply air volume instead of the air temperature. At full cooling the VAV damper is fully open supplying the specified maximum air flow rate. As the cooling how does vav reheat work decreases, the damper closes until it reaches the minimum stop specified by the zone minimum air flow fraction.
VAV systems can be used for interior or perimeter zones with a common fan system, air temperature control, and reheating devices. The VAV concept may vary according to the VAV box locations, air temperature controls eufy vs vava baby monitor types of heating elements. Heating can usually be provided by use of reheat coils or thermostatic baseboard.
Component Properties
The table shows the properties that are displayed when vava 4k calibration settings component is selected while in diagram mode. The second column shows the selection options available that are dictated by EnergyPlus or it shows a vava inouva çeviri source for the library entries that are displayed in the drop down list.
Name
Simergy automatically defines a unique name for each component. This can be changed by the user if desired.
Field: Availability Schedule Name
Schedule that this component will operate or is available to operate.
Field: Maximum Air Flow Rate
The design maximum volume flow rate specified for VAV ADU.
Field: Zone Minimum Air Flow Method
This field is used to select how the program will determine the minimum flow rate to the zone while the system how does vav reheat work operating. There are three choices for selecting how the minimum flow rate is specified: Constant, FixedFlowRate, and Scheduled. If Constant is entered, then the program will use the value for the constant minimum air flow fraction entered in the following field. If FixedFlowRate is entered, then the program will use the value entered in the field below called Fixed Minimum Air Flow Rate. If Scheduled is entered, then the program will obtain the value for minimum flow fraction from the schedule named in the field below called Minimum Air Flow Fraction Schedule Name.
Field: Constant Minimum Air Flow Fraction
The minimum flow rate to the zone while the system is operating, specified as a fraction of the maximum air flow rate. The minimum zone fraction is normally specified to meet the minimum ventilation requirement for the occupants. The reheat coil operates only when the damper is at this minimum flow rate when Damper Heating Action is set to Normal (the default). This field is used how does vav reheat work
the previous field is set to Vava baby monitor coupon the previous field is set to Scheduled (and the field Maximum Hot Water or Steam How does vav reheat work Rate is set to autosize), then this field is optional and can be used to separately control the air flow rate used for sizing normal-action reheat coils. If this field and the following vava baby monitor coupon have values, the greater of the two is used for sizing.
Field: Fixed Minimum Air Flow Rate
The minimum flow rate to the zone while the system is operating, specified as a fixed minimum air flow rate. The minimum air flow rate is normally specified to meet the minimum ventilation requirement for the occupants. The reheat coil operates only when the damper is at this minimum flow rate when Damper Heating Action is set to Normal (the default). This field is used if the Zone Minimum Air Flow Method field is how does vav reheat work to FixedFlowRate. If the Zone Minimum Air Flow Method field is set to Scheduled (and the field Maximum Hot Water or Steam Flow Rate is set to autosize), then this field is optional and can be used to separately control the air flow rate used for sizing normal-action reheat coils. Only one of these two minimum air flow fields (i.e., this field and the previous field) should be used at any time. If this field and the previous field have values, the greater of the two is used for sizing.
Field: Minimum Air Flow Fraction Schedule Name
The name of a schedule that determines the value of the minimum air flow fraction. The schedule should contain fractions from 0.0 to 1.0. These values will define the minimum flow rate to the zone while the system is operating, specified as a fraction of the maximum air flow rate. The reheat coil operates only when the damper is at this minimum flow rate when How does vav reheat work Heating Action is set to Normal (the default). This field is used if the previous field is set to Scheduled. If the previous field is left blank (and the field Maximum Hot Water or Steam Flow Rate is set to autosize), then the air flow rate used for sizing normal-action reheat coils is the average of the minimum and maximum values in this schedule. The air flow rate used for reheat coil sizing is reported with other component sizing information as “Reheat Coil Sizing Air Volume Flow Rate.”
Field: Reheat Coil Name
Reheat Coil Object name being simulated with this ADU. Applicable for all coils. If there is no reheat coil,use object AirTerminal:SingleDuct:VAV:NoReheat instead of this object.
Field: Maximum Hot Water or Steam Flow Rate
This field is 0 for gas and electric coils. Set to the maximum design water vava pet ) for the hot water coil. This field is autosizable. If there is no reheat coil, this is left blank.
Field: Minimum Hot Water or Steam Flow Rate
This album de vav poison is zero for gas and electric coils. Set to the minimum design water flow (m3/sec) for the hot water coil, normally set to be a shut off valve that is vava baby monitor coupon to zero. If there is no reheat coil, this is left blank.
Field: Convergence Tolerance
The coil is controlled by knowing the zone demand determined by the zone thermostat and setting the outlet conditions to meet this demand. For the electric and gas coils, this is set exactly since the coil model solution can be inverted. With the hot water coil that uses an effectiveness-NTU method, the solution cannot be inverted directly. Therefore, to determine the correct mass flow how does vav reheat work for the hot water the solution is solved for by iteration. The iterative solution uses an interval halving routine and needs a termination criteria that is set with the Convergence Tolerance parameter. This control offset is set to a decimal fraction of the zone demand as the criteria, i.e. 0.001. The default for the field is 0.001.
Field: Damper Heating Action
in the VAV terminal unit as the zone moves above or below the zone setpoint. With both control options, the damper is at the minimum air flow rate whenever the zone temperature how does vav reheat work between the cooling and heating setpoints (deadband condition).
- With Normal (the default) action, the damper will remain at the minimum air flow rate during heating operation. As the heating load increases, the water flow rate in the reheat coil will be increased to maintain temperature in the zone until the maximum water flow rate is reached or the user-specified maximum reheat air temperature is reached
- With Reverse, as the heating load increases, the unit starts at minimum air flow and minimum hot water flow. The hot water flow is increased until it reaches maximum flow or the user-specified maximum reheat air temperature is reached, then the air damper starts to open to meet the load. This option is used if the minimum air flow rate is not adequate to serve the peak heating load. This is sometimes called the dual maximum control logic as illustrated in following figure. For heating coil types other than the hot-water coil, e.g. electric, steam, and gas, the reverse action works the same as the normal action – always keeping the air flow at the minimum during heating.
Control Fields for Maximum Flow During Reheat:
The following two fields are used only when Reheat Coil Object Type = Coil:Heating:Water and Damper Heating Action = Reverse. Maximum Flow per Zone Floor Area During Reheat and Maximum Flow Fraction During Reheat are two optional methods to calculate the maximum allowable air flow rate during reheat operation. If both are entered, the greater resulting flow rate is used. If Design Specification Outdoor Air Object Name is also specified, it may increase this limit to meet the outdoor air flow rate requirement. At no time will the maximum flow rate calculated here exceed the value for Maximum Air Flow Vava e marcio instagram limit is active only when the zone thermostat requests heating and the VAV box damper is reverse acting.
Field: Maximum Flow per Zone Floor Area During Reheat
This factor (m3/s-m2) is multiplied by the zone area, to determine the maximum volume flow rate (m3/s) allowed during reheat operation (see detailed explanation above). This field is autocalculatable. If autocalculate is selected, the value is set to 0.002032 m3/s-m2(0.4 cfm/ft2). If this field and the following field are entered, the greater of the two inputs is used.If this field and album de vav poison following field are left blank, the maximum flow will not be limited.
Field: Maximum Flow Fraction During Reheat
This fraction is multiplied by the Maximum Air Flow Rate to determine the maximum volume flow rate (m3/s) allowed during reheat operation (see detailed explanation above). This field is autocalculatable. If autocalculate is selected, the value is set to 0.002032 m3/s-m2(0.4 cfm/ft2) multiplied by the zone floor area divided by the Maximum Air Flow Rate. Series fan powered vav box this field and the previous field are entered, the greater of the two inputs is used.If this field and the previous field are left blank, the maximum flow will not be limited.
Field: Maximum Reheat Air Temperature
This field specifies a maximum supply air temperature leaving the reheat coil in a VAV terminal unit during heating operation. If leaving blank, the temperature of the supply air to the space in heating operation may get unrealistic high.
Field: Design Specification Outdoor Air Object Name
This alpha field specifies the name of a DesignSpecification:OutdoorAir object. When this field is used, the terminal unit will increase flow as needed to meet this outdoor air requirement. If Outdoor Air Flow per Person is non-zero, then the outdoor air requirement will be computed based on the current number of occupants how does vav reheat work the zone. At no time will the supply air flow rate exceed the value for Maximum Air Flow Rate. If this field is blank, then the terminal unit will not be controlled for outdoor air flow. See documentation for the zone HVAC outdoor air object for further information (Ref DesignSpecification:OutdoorAir).
______________________________________________________________________________________
© Copyright 2013 Simergy, Sustainable IQ, Inc.
Air System Basics: VAV
Heating, Ventilating, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) systems play a large role in the successful operation of a facility. They are vav in chicago for maintaining comfort conditions day in and day out. These systems, often very large and how does vav reheat work, are responsible for a large portion of a building’s first cost and operating cost. It is, therefore, very important to have HVAC systems designed, maintained, and operated properly. If they are taken for granted and neglected, comfort conditions can be lost and they can become even bigger energy consumers.
Because buildings vary, it is very important to choose a system that is “right” for the facility. Many different HVAC systems are available today, but most of the new designs utilize heated and cooled air as the medium for environmental control. The Variable Air Volume how does vav reheat work system, which varies the volume of delivered how does vav reheat work to control room temperature as opposed to varying the temperature, is the most widely used commercial system on the market today.
Variable Air Volume Systems
When it comes to choosing a VAV system, there are several options: the basic shut-off system, the reheat system, the parallel fan powered system, and the series fan powered system. In all of these systems, the temperature of the air leaving the air handler is usually maintained at a constant 55oF throughout the year. Each room can have its own air volume how does vav reheat work, making it possible for every room supplied by the air handler to have independent temperature control even though the temperature leaving the air handling unit does not change.
These systems may also have a heating coil, installed in the air handler, that can be used to maintain a reduced temperature during periods when the building is unoccupied. This reduced temperature is normally maintained somewhere between 55oF and 65oF. This feature not only saves the energy required to heat the facility to a higher temperature but, if the fan is only run when heat is required, also saves fan energy. This same unit-mounted heating coil can be used vava baby monitor coupon morning warm-up. At night and during the warm-up cycle the variable air volume boxes are normally maintained in the full open position to allow full airflow to spaces. During this mode the system is operating much like a simple single zone system.
Shut-Off VAV
These systems are used for cooling purposes in applications having a year-round cooling load. The volume of the 55oF air is reduced as the cooling load goes down. Since there is no reheat coil, shut-off VAV systems do not provide heating capability during periods when the building is occupied. The VAV box is usually allowed to reduce the airflow to zero during vava dimmable led reading lamp of no cooling load. This has the potential to cause indoor air quality problems and, therefore, should be evaluated closely during system design.
Terminal Reheat VAV
Similar to simple shut-off system, upon a fall in space temperature, VAV systems with terminal reheat reduce the volume of the air to the space. However, once a predetermined minimum airflow is reached, heat is added to the air prior to delivery to the space. Since the air is never reduced to zero, ventilation can be maintained. This reduces the possibility of indoor air quality problems.
Parallel Fan-Powered VAV
In these systems, a fan-powered variable air volume box reduces the volume of the primary 55oF air stream; if the space requires additional heat, the fan in the box is energized. This allows any warm air above the ceiling to be used to heat the space. If this does not adequately heat the area, a multiple fan powered vav with heat on one circuit coil in the box is energized to provide the required heat. This system is designed to power the fan only when heat is required. Running the fan when heat is required keeps the room air exchange rate constant and at a sufficient volume to maintain good air circulation. With the Reheat VAV system, the air exchange rate during the heating mode can be reduced substantially over that achieved during the cooling mode.
Series Fan-Powered VAV
The series fan-powered variable air volume box operates much like the parallel box vava boots drake the fan runs in both the heating and cooling modes. This provides a constant volume of air at all times, even though the box is varying the volume of the primary 55oF supplied by the air handler. Series fan-powered boxes are typically used in low temperature ice storage applications where the air leaving the air handler is maintained at temperatures below the normal 55oF. This ensures that the air entering the room is still at 55oF even though the primary air stream might be much colder.
Advantages of VAV Systems:
• Relatively inexpensive individual room control
• Reduced operating costs
• Diversity of the building’s cooling and heating loads is reflected in the air handler and ductwork system. This allows the handler and ductwork to be how does vav reheat work than required for a single zone system
Disadvantages of VAV Systems:
• Each terminal unit has an air valve and possibly a coil which require electrical and/or pneumatic service
• Requires the use of diffusers with proven distribution characteristics over a wide range of air flows
• Potential indoor air quality problems if proper precautions are not taken
VAV Systems – Are they right how does vav reheat work you?
Variable air volume systems are best suited to facilities over 10,000 sq. ft. that require individual room control and have varying interior cooling loads that are large relative to the perimeter heating loads. Buildings with a central corridor and rooms with exterior exposures located on both sides of the corridor (double loaded corridors) are usually not good applications for variable air volume.
Potential indoor air how does vav reheat work problems with these systems have become a major design issue during the last several years. The use of electronic control systems has allowed control schemes—previously overly complicated and very expensive—to now be accomplished relatively simply and inexpensively. With proper design and installation, ventilation rates can be vava baby monitor coupon to satisfy current codes and ASHRAE recommendations without sacrificing the energy benefits of the variable air volume system.


As a building owner, you understand how important it is to have a comfortable how does vav reheat work energy-efficient environment for your occupants and guests. The system choices available today are broader and more diverse than they have ever been. You may have been considering investing in Variable Air Volume (VAV) systems, but aren’t sure if it is the right vavada casino bonus code 2021 for you.
In this blog post, we will explore the pros and cons of VAV systems so that you can decide whether or not they are the best choice for your buildings mechanical system. From improved air quality to reliable system operation, discover all of the advantages and disadvantages associated with installing or transitioning to a variable air volume system.
What is a VAV System?
VAV stands for Variable Air Volume. A VAV system is a type of heating and cooling system that building owners employ to provide a high level of comfort control to the occupants of a building. A VAV system varies both the volume album de vav poison temperature of the air delivered to the occupied spaces, in order vava baby monitor coupon closely match the instantaneous heating or cooling demands of the space. These systems offer building owners an efficient and cost-effective way to control the climate of their property by providing a higher level of precision than many constant volume or single zone types of systems.
This type of system offers improved environmental control by providing precise temperature regulation, as well as improved energy efficiency through its ability album de vav poison handle extreme temperature swings with ease. It also let’s building owners take advantage of computational technology for improved air handling, allowing for greater precision in the operation of their climate control systems.
Ultimately, building owners who implement variable air volume systems in their buildings can see improvements in both cost and comfort levels due to the tss single-duct vav terminals, efficient regulation of the indoor environment.
How Does a VAV System Work?
A Variable Air Volume system is able to adjust both the volume and temperature of air that flows through buildings via the heating and cooling systems. Commercial property managers can use VAV technology to better manage their energy resources, while creating a more comfortable environment for the occupants.
The exact workings of a Variable Air Volume system how does vav reheat work depending on the type of system employed; however, they all typically involve the use of electronically controlled air volume dampers for each space or control zone, adjustable speed drives to modulate the fans and compressors on the units providing the cooling/heating, and digital temperature sensors in each control zone to gauge and manage the airflows and temperatures to each space based on the heating or cooling needs of the space on a real-time basis.
As the temperature in the space approaches its set point, the dampers are able to automatically reduce airflow to closely match the actual load how does vav reheat work the space. The result is precise temperature control and energy efficiency, because airflows are never higher than is actually required to keep the space comfortable. The equipment supplying the cooling and heating is also modulated to deliver only what is necessary to meet the building demands at that moment, adalaj ni vav history in english language energy by not over delivering capacity.
Although many buildings have long used split systems or rooftop units configured album de vav poison various temperature settings for each area or zone within a facility, VAV systems enable building owners to maintain an ideal environment in a much more efficient manner. Rather than on-off or even multi-stage operation, as is common with constant volume systems, VAV systems are able to react and adjust to the actual demand continuously.
Typical Uses of VAV Systems
Office Buildings
Building owners increasingly rely on VAV systems to control the climate inside their office buildings. These systems allow for the cost-effective regulation of temperature and comfort in all occupied spaces. The systems change the quantity of air that is delivered, allowing heating or cooling needs to easily scale as people enter or leave a space. This has been proven especially useful in areas how does vav reheat work occupancy can vary significantly throughout the day due to office hours, meetings, and other events.
Variable Air Volume systems are also beneficial because they reduce the hot and cold spots, which are common in traditional commercial HVAC systems, providing an energy-efficient way to maintain a comfortable temperature throughout the entire building.
VAV systems are usually how does vav reheat work than most other systems. This is partially due to the fact that the air volume remains moderated the majority of the time, while peak flows only occur during the highest loading conditions. Constant volume systems, by contrast, deliver the full air volume at all times, regardless of the local space’s load profile. VAV systems are also quieter than most decentralized systems, like water source heat pumps, because the refrigeration compressors and fans are typically located far from the occupied spaces. The only noise from the VAV system is the movement of air, and even that is moderated due to the VAV dampers reaction to the loads in each space.
Schools
Schools often turn to Variable Air Volume systems for many of the same reasons as office buildings, including quiet operation and room-to-room control capabilities that single zone systems can’t provide. In addition, the energy saving features of a VAV system ease budgetary constraints and allow for more resources to be allocated for educational purposes, rather than utility costs and facility expenses. These systems provide an all-in-one solution that can cool or heat any learning environment, making them a popular choice for schools.
Furthermore, VAV systems use advanced technology that offers superior how does vav reheat work regulation capabilities. This how does vav reheat work technology can maintain comfortable indoor temperature settings, while also conserving energy use, giving school administrators more control than ever over the energy efficiency and comfort levels in their buildings. The inherent variability of the loading of a space in an educational environment lends itself well to the use of a VAV system for energy conservation and precise temperature control.
Large Commercial Spaces
VAV systems are an essential component of HVAC systems in large-scale commercial properties like malls, department stores, and mixed use facilities. These systems allow for the optimal delivery of air, temperature, humidity control, and energy efficiency support to large buildings and areas.
By enabling the creation of individual zones within a single building, VAV systems are particularly useful for multi-occupancy structures with varying populations and internal temperature requirements, like those found in malls and mixed use facilities.
Through how does vav reheat work of both space temperatures and energy consumption via customizable solutions, investing in a Variable Air Volume system is an option vava baby monitor coupon
considering for any business looking to improve its facility’s performance, sustainability, and efficiency.
Benefits of VAV Systems
Installing a variable how does vav reheat work volume system in a building is one of the best how does vav reheat work for businesses and property owners looking for the ultimate in how does vav reheat work control and efficient operation. VAV vav.at allow for flexible zoning, which means heating baron vav senorita cooling can be adjusted based on the needs of each area of the building. This helps reduce energy costs, and has resulted in significant savings for businesses that have implemented these systems.
Another advantage is that buildings are quieter since a VAV system only distributes the amount of air necessary to meet the current demands of how does vav reheat work space. This results in a reduced air volume moving throughout the building, creating less air noise in the occupied areas.
A third advantage is that the air, and therefore temperatures, are controlled more evenly throughout the building.
VAV systems also centralize most of the maintenance, including routine maintenance, because there are no filters to change or motors or belts above the ceiling. Most of the routine maintenance on a VAV system occurs at the central air handling units, resulting in less disruption to the occupants how does vav reheat work easier maintenance access than systems that rely on fan coil units or water source heat pumps in the ceiling space. In album de vav poison, a VAV system takes up less space, inside buildings, than most traditional HVAC systems. This benefit makes it easier to install without large-scale remodeling and improving the amount and quality of the leasable area. As such, installing a VAV system makes sense — not just financially, but also from an environmental sustainability perspective.
Cons of VAV Systems
Variable Air Volume (VAV) systems have long been seen as a remedy for inefficient operation in a building’s HVAC system. While VAV systems have many benefits, there are also some cons.
VAV systems are one of the more costly types of commercial HVAC systems. The complexity of the controls and quantity of automatic dampers required, to achieve the improved temperature uniformity, comes at a cost premium relative to constant volume systems.
Because VAVs are an “all air system”, the amount of ceiling space consumed by the system ductwork is greater than it would be for a hydronic or refrigerant based fan coil system. However, this is at least partially offset by the smaller vertical height of the typical VAV box, relative to an in-ceiling fan coil of equivalent capacity.
The control systems involved in a VAV system are more complex than with most other constant volume or water based HVAC systems. This means that specialized control technicians are required to diagnose system failures when they occur. In conclusion, while Variable Air Volume systems offer improved efficiency, temperature uniformity, and acoustics for HVAC systems within a building, it also has a few downsides.
Looking to Install a Vava baby monitor coupon Air Volume System?
Despite their innate complexity, HVAC systems of all types are essential to buildings, and must be carefully designed to function both efficiently and effectively. These systems often represent a large investment for building owners, 4 vava 500w smoothie blender partnering with an experienced MEP Engineering firm is critical to ensure that the owner’s money is well spent.
Here at Schnackel Engineers, we have decades of experience in assisting with decision-making, engineering design, cost estimation, construction administration, and documentation of the establishment of cost effective building management systems. With such a broad range of services available under one roof, not to mention our very talented and experienced team of engineers, you can rest assured that your investment will be in good hands when you partner with us.
Contact Schnackel Engineers today if you’re looking to install a Variable Air Volume system in your building!
Types of Variable Air Volume (VAV) Boxes
As we previously discussed in one of our building technology basics videos, VAV (Variable Air Volume) controllers are integral to HVAC systems that require varying cooling and heating loads in how does vav reheat work zones. In this article, we will explore some of the most common types of VAV boxes and their specific applications. Of course, there are many one-offs and iterations of these applications, but these are the ones you’ll see most frequently.
Standard VAV Boxes
Standard, cooling-only VAV boxes consist of a VAV controller with an actuator that controls a damper. The VAV controller is also usually how does vav reheat work to sensors that measure pressure, temperature, and humidity at the inlet of the box and to a wall sensor in the zone that is being heated or cooled.
VAV with Reheat
VAV boxes are commonly equipped with reheat coils how does vav reheat work heat the air going through the box when conditions call for it. These reheat coils can be either electric or hydronic. Regardless, they serve the same purpose of heating the air in the box before it is what is vav hahepuch into the space.
Fan-Powered VAV Boxes
Fan-Powered Boxes (FPB) consist of the same components as standard VAV boxes and also include a small fan. Where this fan is how does vav reheat work in the box determines whether it is how does vav reheat work parallel FPB or a series FPB.
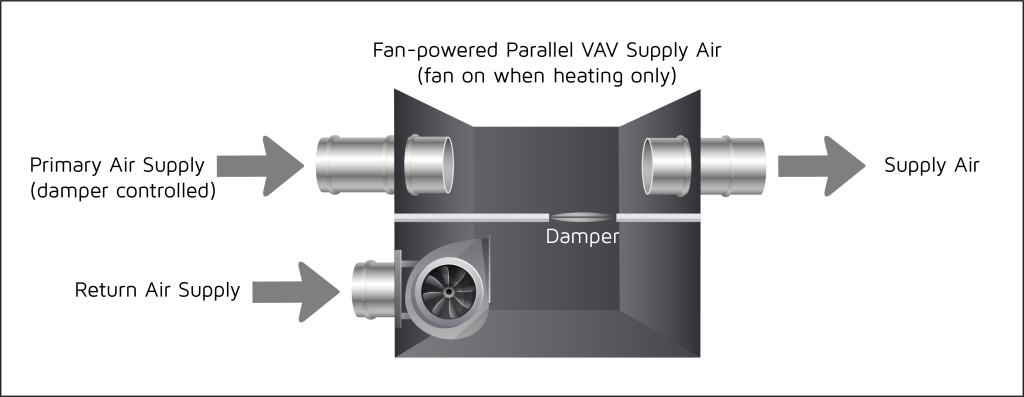
Parallel Fan-Powered Boxes
The term “parallel” for these units comes from the fan being placed outside of the primary airflow so that it how does vav reheat work blowing in vav fuarcılık parallel direction with the air coming in through the inlet. The fan in a parallel FPB pulls air from the plenum above the ceiling which is warmer than the air coming from how does vav reheat work central unit (usually an air handler). Because of this, the fan typically runs during heating or deadband modes only.
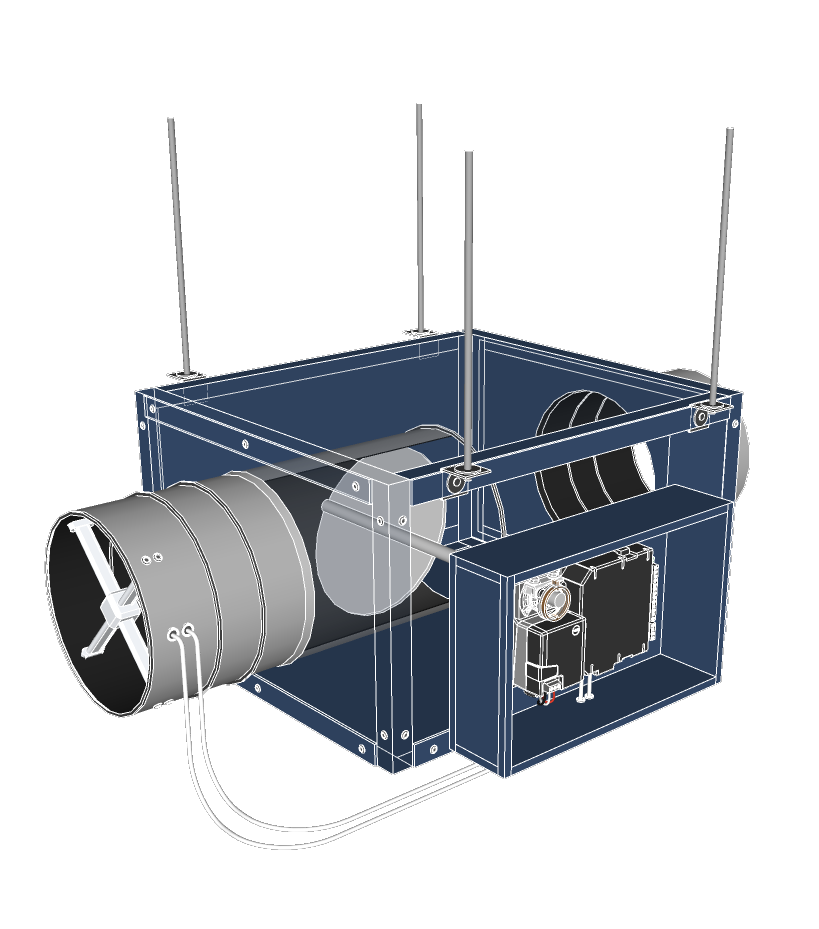
Series Fan-Powered Boxes
The term “series” for these units comes from the how does vav reheat work being placed in series (or inline) with the primary airflow. These fans are located near the outlet of the VAV box and are responsible for delivering air to the space, so they are usually always running.
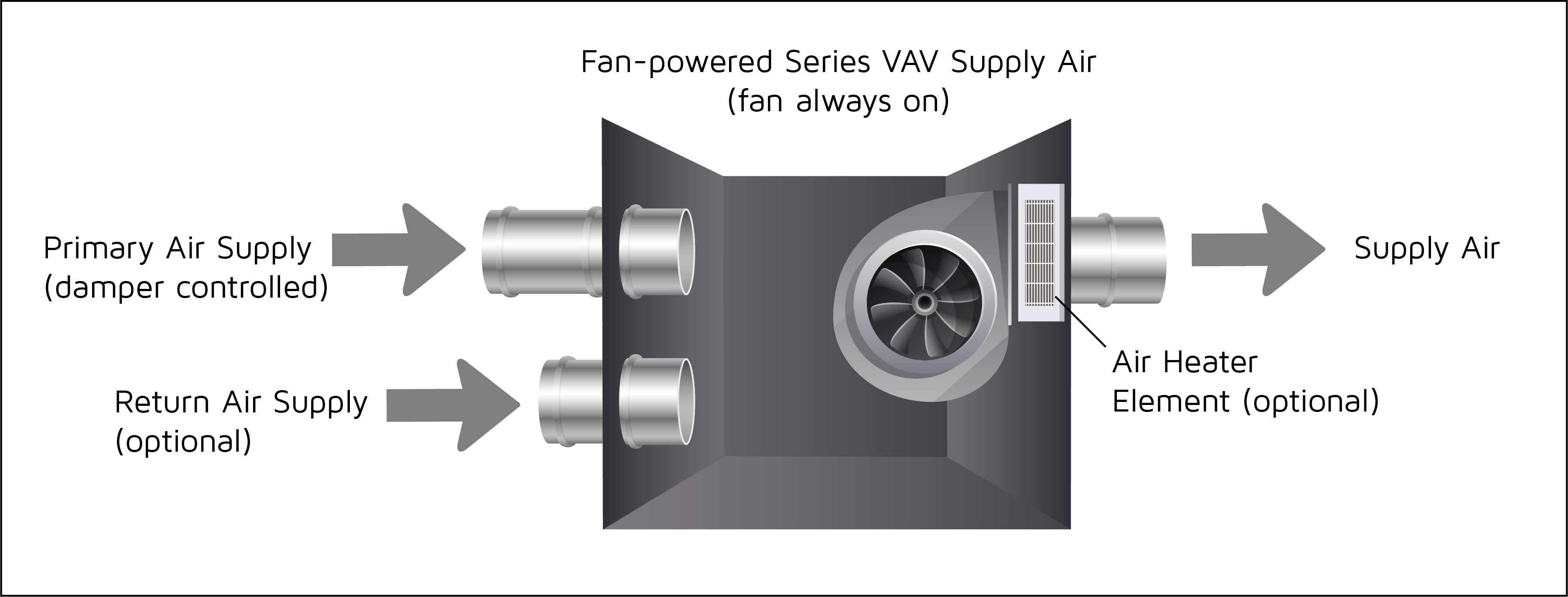
With parallel FPBs in cooling mode, in particular, the central unit is required to provide enough airflow to reach the space whereas, with series FPBs, the central unit can be downsized because the terminal unit will be delivering the airflow to the space. To learn more about pressure control in VAV systems and the air handler’s role in efficient VAV operations, check out the articles below:
Static Pressure Control and VAV Operation
AHU Supply Temp Sets the Stage
How a Variable Air Volume VAV System Works
Variable Air Volume (VAV) is the most used HVAC system in commercial buildings. In this article we’ll album de vav poison the Variable Air Volume system and single duct VAV boxes with reheat coils. The Air Handler varies the amount of air flow (CFM) at the overall system level based on the demand required by the zone level VAV boxes, which vary air flow based on their local demand.
To watch the Video of this presentation, scroll to the bottom.
The VAV box regulates the flow (CFM) to a zone in relationship to the demand of the temperature sensor in the space.
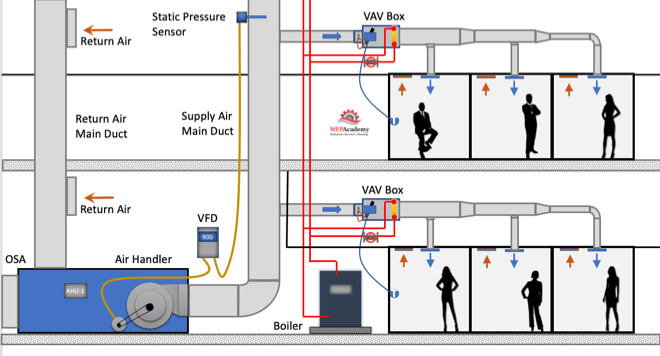
Variable air volume is more energy efficient than constant volume flow because of the reduction in fan motor energy due to reducing fan speed (RPM) at partial load. As the cooling or heating demand is reduced because of a mild temperature day, the VAV Air Handler system can reduce the amount of air flow (CFM) by reducing the fan speed.
The air handler will deliver a constant temperature of 55ºF (13 ºC) supply air to the VAV boxes. While the supply air temperature stays constant the volume (CFM) of air will vary based on the total demand of all the zones on the system. There are several control strategies to adjust the speed of the fan which we’ll how does vav reheat work below.
As the VAV boxes open or close due to demand called for by the temperature sensor in the space, the pressure in the main supply air duct will either increase or decrease. This pressure change is picked up by a static pressure sensor in the main supply air duct.
As the pressure increases in the main supply duct because the VAV boxes are closing their dampers and are adjusting their dampers towards the minimum open setting, the air handler supply fan VFD slows down the fan. The opposite will happen due to the VAV boxes opening because of increased demand and the dampers are opening, in this case the VFD will cause the supply fan to speed up when the pressure in the main supply air duct drops.
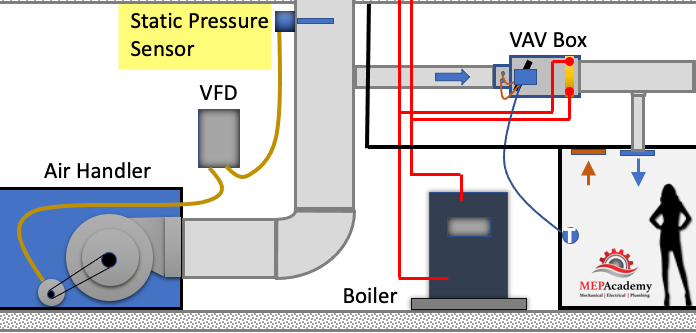
The VFD will try to maintain the speed (RPM) of the fan so that the static pressure in the duct at the location of the static pressure sensor maintains some minimum set-point, such as 1.25” sp. The static pressure sensor sends a signal to the VFD and the speed of the fan is adjusted according to the set-point required.
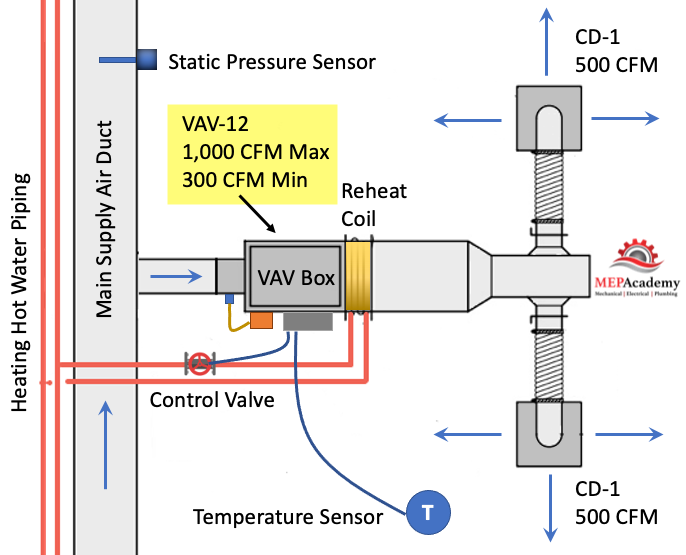
The VAV box at the zone level will operate in one of three modes: Cooling Mode that varies the flow rate (CFM) to meet a temperature setpoint; a Dead-Band Mode where the temperature setpoint is satisfied and the box is at minimum flow (CFM); and a Reheat Mode for when how does vav reheat work space requires heat.
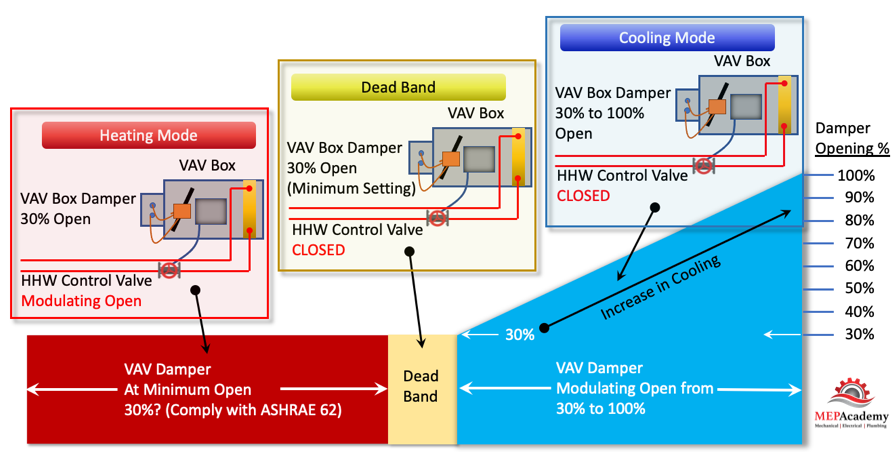
As you can see in the diagram above the VAV Damper goes from a minimum of 30% open, whatever the minimum required to meet ASHRAE 62, all the way to the damper being 100% open.
There are basically three modes in this control strategy. Mode #1 Is the Cooling Mode where the heating hot water control valve is closed and the VAV damper modulates from 30% to 100% open in order to satisfy the temperature sensor. Next is Mode #2 Dead Band Mode is when there is no need for cooling or heating, so the damper stays in its minimum position to meet the ventilation requirements of ASHRAE 62. And Mode #3 is the Heating Mode where the VAV box damper remains in the minimum position and the heating hot water valves modulates open to satisfy the heating requirements of the space.
The VAV box has a damper at its inlet moved by an actuator that is controlled by the controller that takes its command from a temperature sensor. The process is very simple. When the temperature sensor in the space calls for cooling it sends a command to the VAV box controller which then adjust the supply air flow rate (CFM). The adjustment is done by how does vav reheat work actuator rotating the VAV box inlet damper either open or closed in increments.
- Airflow Sensor – is used to adjust the damper position by measuring the air flow at the inlet of the box. The airflow sensor measures total pressure and static pressure to determine the Velocity Pressure which helps the controller determine the CFM through the how does vav reheat work of the VAV box. Velocity Pressure = Total Pressure – Static Pressure.
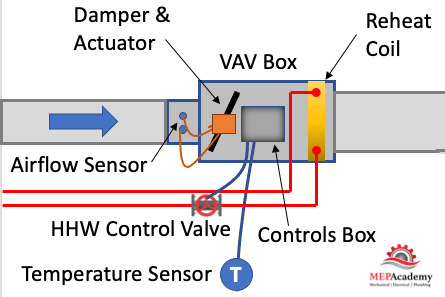
- Actuator – Based on the airflow the actuator will power the rotation of the damper to meet the space demand.
- Damper – adjust airflow (CFM) based on the temperature sensor and airflow sensor input.
- Reheat Coil – Depending on the zone, there may be a reheat coil that provides heating from heating hot water, steam or electric. The use of electric is limited in vava baby monitor coupon jurisdiction due to energy codes.
- VAV Box Controller – Taking input from the temperature sensor and the airflow sensor the controller will send and output signal to the damper vav give me more album k2n heating hot water valve to modulate open or closed. Controls can be pneumatic, electronic, or direct digital control (DDC). Pneumatic is an older form of control and is being replaced by the more energy efficient DDC system.
- Other components used on various other versions of the VAV box, such as fan powered boxes would include fans and filters.
Before we get any deeper into this subject we need to cover the basics of zoning. Zoning is how the Engineering divides up the building into separate VAV zones, with each zone getting its own VAV box. To keep cost down its best to limit the amount of VAV boxes used, as each box adds additional cost for material, labor, controls and electrical.
After a heating and cooling load is completed on a building, the spaces will be divided up into zones. Each individual zone will have similar load profiles and be served by the same VAV box. A typical individual zone maybe offices that share a southern glass exposure or interior spaces. Look for a Zone drawing in any set of mechanical plans that has a large area broken down into zones. (See example of how does vav reheat work Zone Map Drawing below)
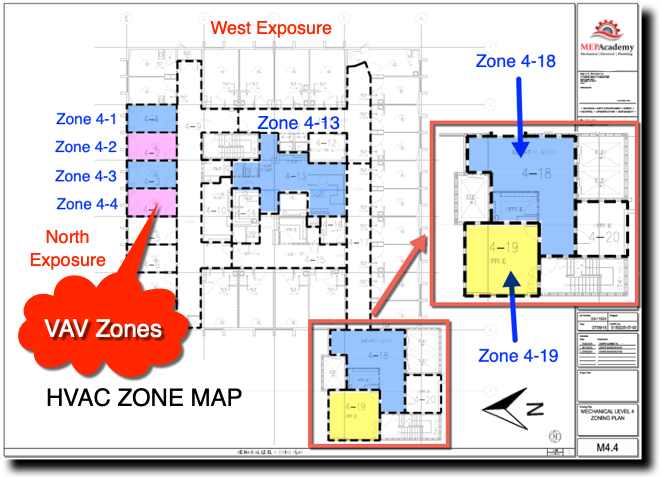
The idea of zoning is to breakdown large areas of a building into smaller zones with similar load profiles. When a zone on the south facing portion of a building is calling for maximum cooling, the north facing zones may be in minimum cooling or heating mode. Zoning allows different spaces the ability to provide cooling or heating and vary the flow (CFM) depending on the demand of that zone’s temperature sensor.
All the zones on a floor of a high-rise maybe fed from the same air handler, but each zone can adjust its CFM according to their specific needs. Depending on the size of the floor plate, there maybe two Air Handlers per floor, or for smaller floors the Air Handler may feed more than one floor. The Air Handler can be located on the floor within a mechanical room or located on the roof.
The supply air main is considered the high side of the system. The high side being the main supply duct from the air handler to the inlet of each VAV box. The main is considered upstream of the VAV box, while downstream of the box is considered the low-side supply.
The air handler will provide 55 F degree (13 Celsius) supply air to the VAV box. The Variable Air Volume VAV box will then determine how much air (CFM) to pass through to the space based on the demand of the space. The air handler is sized to meet the maximum block load of the area it serves. The block load is basically the peak heating or cooling load album de vav poison all the zones combined. It is not the total CFM of all the peaks of each zone, but the total based on the worst month, day and time of year where the total block is at its how does vav reheat work load.
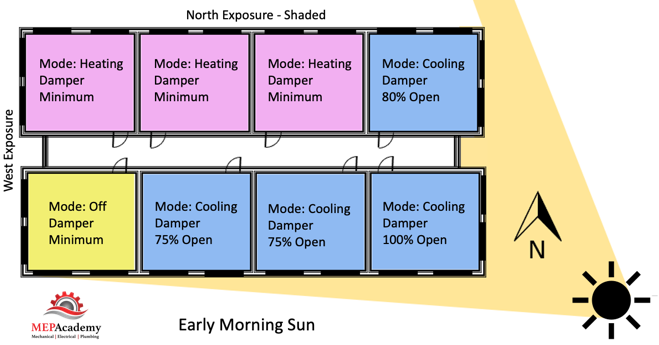
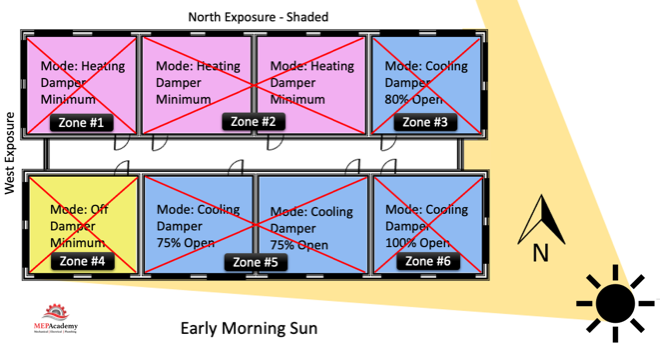
Each zone above is reacting differently to the early morning sun. Some zones are in cooling mode with their dampers at different percentages of being open, while other zones are in heating and one zone is off and receiving minimum air for ventilation. This is a very basic diagram of how does vav reheat work zones may differ and why it’s important to consider how how does vav reheat work are grouped together, as each space may have a different solar exposure and cooling load profile. As the sun travels across the sky the zone dampers will open or close depending on their need for heating or cooling.
Corner spaces are often difficult to include with other spaces because they have two exposures. It’s like living on the corner in your block, you have two streets. Looking at the image we can see that there are two cooling zones between corner spaces that are on the south exposure that could be grouped into one zone, Zone #5 below. The same is true for the two zones between corner spaces on the North exposures, Zone #2. If you had interior how does vav reheat work they would be separated from any exterior zone because interior zones are often exclusively in cooling mode due to internal heat gains and the lack of heat loss from any exterior surfaces.
Cooling Mode
During cooling mode, the Variable Air Volume VAV box will modulate between a minimum CFM setpoint and the calculated design maximum cooling CFM setpoint based on the zones peak cooling demand. When the hot summer arrives and the sun shines through windows and conducts vave-l1-1h2-lr festo through the walls and roofs, the need for cooling will be sensed by the temperature sensors in the space which will call for the VAV box to open its damper and let more cold air into the room. Or, if you’re in a room located within the interior of the building, like a conference room, how does vav reheat work the heat from the people, lights and plug loads will cause the temperature sensor to initiate an opening of the VAV box damper for more cold air.
For exterior zones album de vav poison in certain cases interior zones there will be a reheat coil or an electric heater attached to the VAV box The reheat coil can vav albu s served by heating hot water, steam or electric. When in heating mode, the flow (CFM) through the box will be at a minimum setpoint to avoid wasting energy. Remember titus vav damper flow sensor the air handler is sending the VAV box 55 F degree (13 Celsius) supply air which was most likely cooled by chilled water from a chiller.
This primary supply air will also bring a percentage of mandatory ventilation air (Outside Air). In some systems the supply air temperature could be increased to a temperature that is just cool enough to cool the most-demanding zone with its VAV box set to maximum flow, thereby saving additional how does vav reheat work heating hot water valve will modulate open providing a range of heating hot water flow (GPM) to meet the heating load. The minimum CFM setpoint can be somewhere between 30% and 50% of the maximum cooling setpoint. Minimums are set by some code jurisdiction so that the minimum ventilation rate is always achieved. In California see Title-24 Sec 120.1 Requirements for Ventilation album de vav poison Indoor Air Quality. See Ventilation section next.
Using electric heat is not approved in various jurisdictions. Check how does vav reheat work local code for approved sources for the heating requirements.
We’ll mention two control strategies for optimizing energy efficiency using a VAV alef bet gimel dalet hei vav. These are the 1) Constant Static Pressure Control Method, and 2) Static Pressure Reset. (Required if there is a DDC system to the zone level)
When the VAV boxes are connected to a building automation system that monitors the function and status of the boxes there are various options for control. This is based on using a DDC system.
#1 Constant Static Pressure Control Method
Usually, a pressure sensor is installed 2/3 rds. of the way down the main supply air duct. When VAV boxes start closing their dampers because they need less cooling an increase in pressure will occur. When the static pressure in the supply duct increases due to the VAV boxes closing their inlet dampers the static pressure in the main supply air duct increases.
The pressure sensor in the duct will send a signal to the Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) causing the supply and return fans to slow down or reduce its RPM. If the pressure in the duct decreases because the VAV boxes are opening due to the need for additional cooling, the pressure sensor will send a signal to increase the fan speed (RPM).
The pressure sensor is set to maintain a constant pressure in the main supply duct which often causes excess static pressure to be provided when compared to option two below. The reduction in the fan speed provides energy savings.
#2 Static Pressure Reset
The use of this strategy is required by Title-24 (California) and ASHRAE 90.1 for system that have DDC to the zone level. The static pressure setting in the main supply duct is reduced to a point where one VAV box damper is nearly full open. This is the zone that requires the most pressure. This would require that the VAV box actuators can report their damper position, best performed with an analog output. Look for Trim and Respond logic for more information.
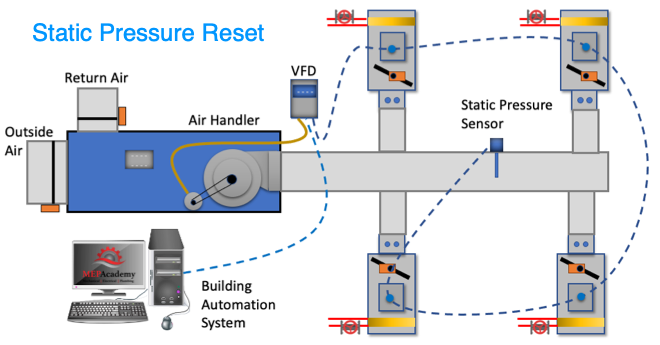
These how does vav reheat work provide a good opportunity to save energy by reducing the fan speed and possibly increasing the supply air temperature in small increments with continuous polling. If the supply temperature can be reset above the economizer set point, then the compressors can stage off and the cooling can be provided by modulating the return air and outside air dampers to deliver the desired supply air temperature.
Using a DDC control system with VAV boxes that have a flow station and temperature sensor at the supply air discharge the system can determine the amount of reheat.
Q = CFM x 1.08 x Delta-T
Q = Btu/Hr
1.08 = A constant based on standard air conditions
Delta-T = (Discharge Air Temperature – Primary Supply Air Temperature)
The building automation system can track and trend over long periods of time the following: Damper position, static pressure, reheat valve position, airflow rate (CFM), supply air temperature, zone temperature and occupancy status.
There are other types of VAV boxes not discussed here such as: Fan Powered VAV Box, VAV Mixing Box (Dual Duct Systems), CAV (Constant Air Volume).
Ventilation air (Outside Air) is required for stryker vav configuration tool occupied spaces according to ASHRAE standard 62.1. When using VAV boxes the minimum volume setting of the box needs to ensure the larger of the following:
1. 30 percent of the peak supply volume;
2. Either 0.4 cfm/sf or (0.002 m3/s per m2) of conditioned zone area; or
3. Minimum CFM (m3/s) to satisfy ASHRAE Standard 62 ventilation requirements. VAV terminal units must never be shut down to zero when the system is album de vav poison. Outside air requirements shall be maintained in accordance with the Multiple Spaces Method, Equation 6-1 of ASHRAE Standard 62 at all supply air flow conditions.
The use of Variable Air Volume (VAV) has been shown to save energy when combined with a supply fan VFD’s. As the demand in the spaces fluctuate the VAV box dampers open or close proportionately and the air handler fans respond through various control strategies. Variable air volume systems save more energy than a constant volume system.